Case Presentation:
AVM R Temporal - Case 1
History & Physical
- 22-year-old right-handed man presented with new onset of tonic-clonic seizure.
- His neurological examination was completely normal.
Imaging
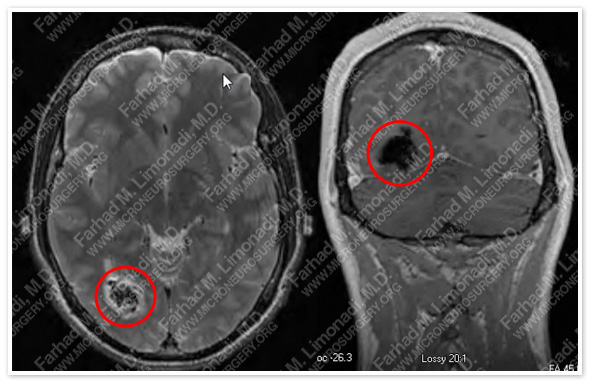
MRI of the brain shows a right posterior temporal arteriovenous malformation (AVM).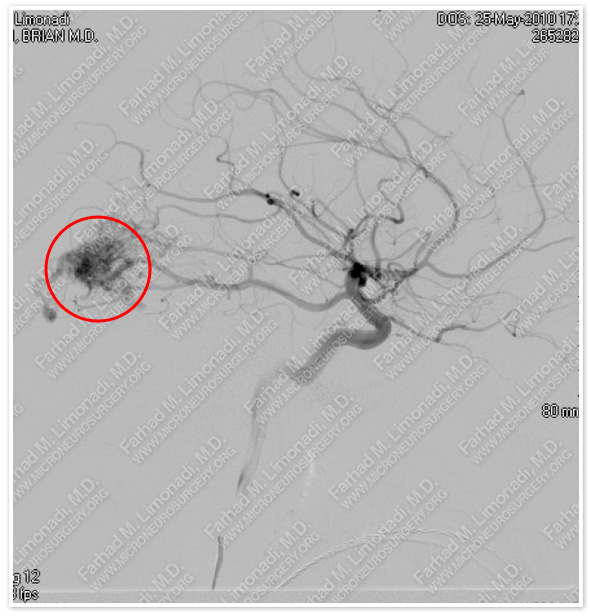
Cerebral angiography shows an AVM primarily supplied by a fetal posterior cerebral artery.
Computer Navigation
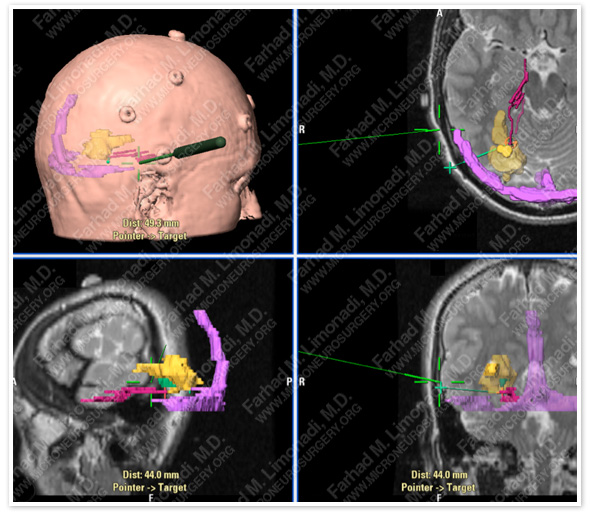
Computer navigation and stereotaxy was utilized to precisely model and map the AVM for surgical planning (yellow). Feeding branches of PCA are shown in red, and transverse and superior sagittal sinuses are shown in pink. Surgical instrument is shown in green.
Surgical Procedure
- He underwent angioembolization of the AVM using Onxy by interventional team with nearly complete exclusion of this AVM from cerebral vasculature.
- He then underwent right temporal craniotomy using stereotaxy and computer navigation, together with intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring.
Pathology
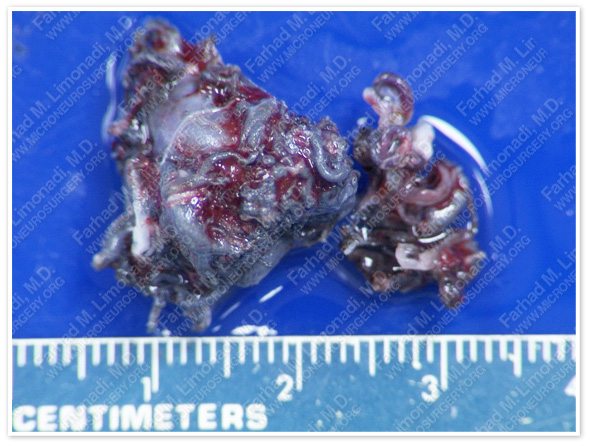
The AVM was removed without any difficulty during surgery and sent for pathological evaluation which confirmed the diagnosis.
Post-op Imaging
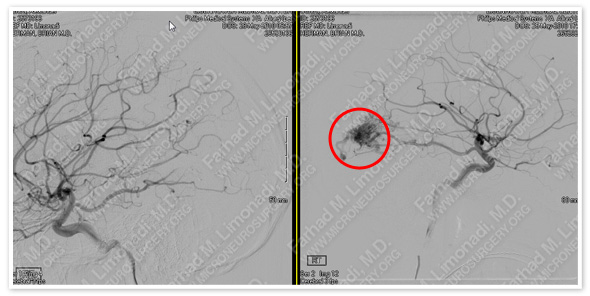
After Operation Before Operation
Post-op cerebral angiography shows no residual AVM and intact normal cerebral vasculature.
Post-op Course
- He did well postoperatively with no neurological deficit with the exception of mild visual field deficit initially, which resolved on follow-up.
- He has since returned to normal function.


















