Case Presentation:
Parkinson's Disease - Case 1
History & Physical

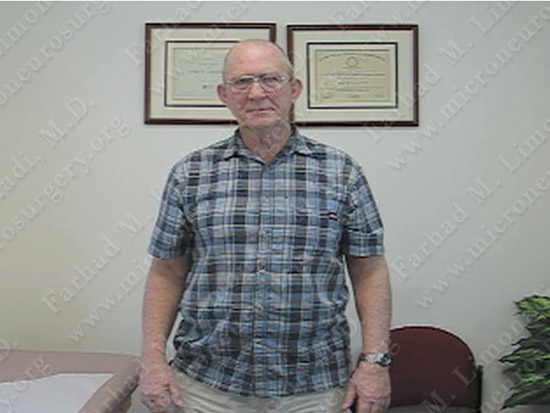
The patient as he appeared in the clinic.
- Patient is a 64-year-old right-handed gentleman with initial diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease ten years prior to presentation. His symptoms were reasonably managed with medical treatment for seven years. Over the past three years, patient had developed significant dyskinesia with motor fluctuations. He had episodes of tremor, alternating with significant and uncontrollable movements of his arms. His wife stated that the intensity of his Parkinson’s syndrome was such that he could not hold a plate or a cup of coffee. He could not tie his shoes. Most of his symptoms at the time involved his left side.
- Patient was a considered a good candidate for implantation of right STN DBS (subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulator).
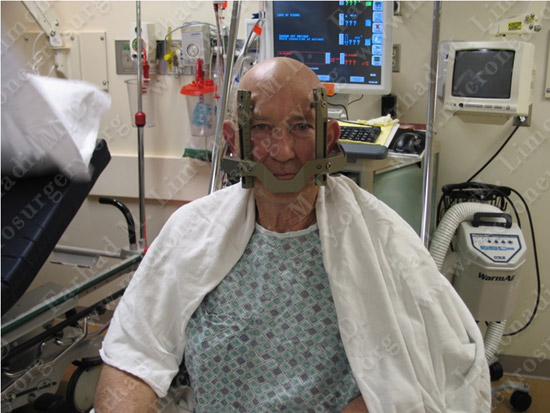
A Leksell stereotactic frame was placed on his head in the pre-op area.
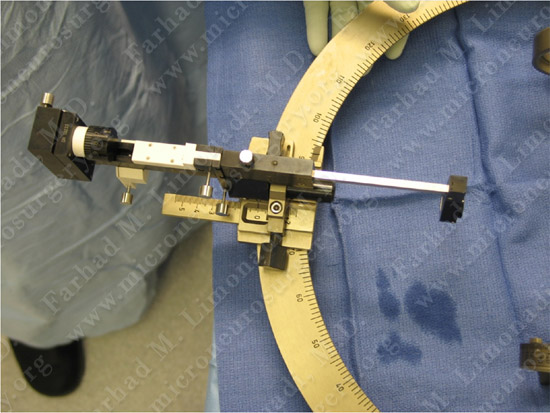
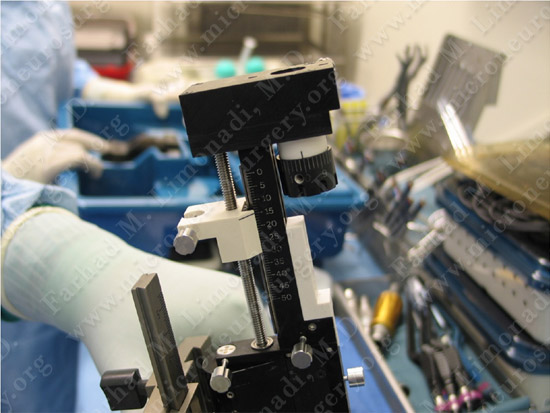
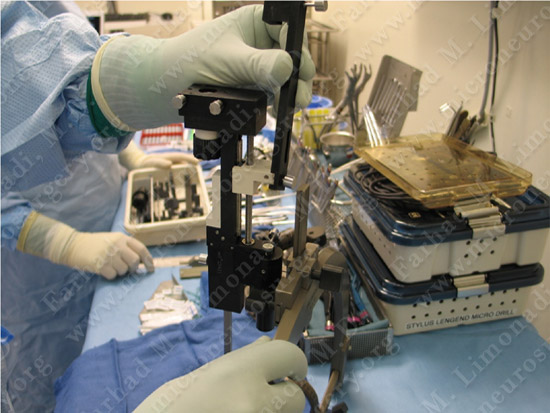



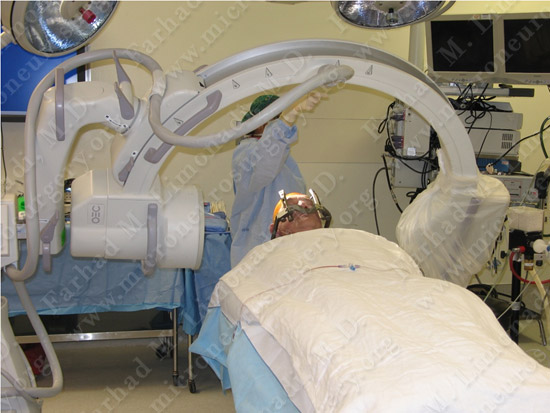
Patient is brought and positioned comfortably in the operating room.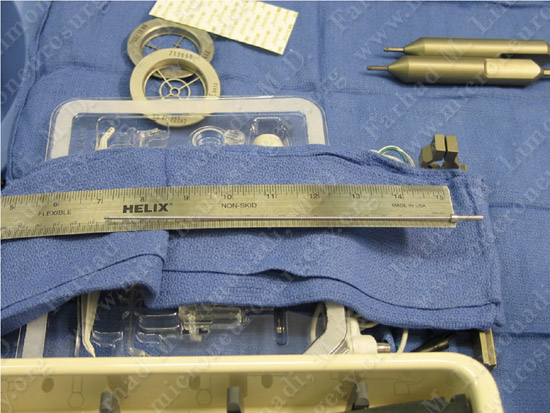
The DBS implantation equipment is being prepared in the operating theater.
Imaging
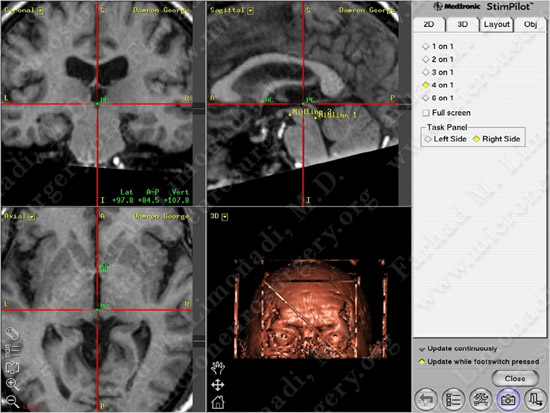
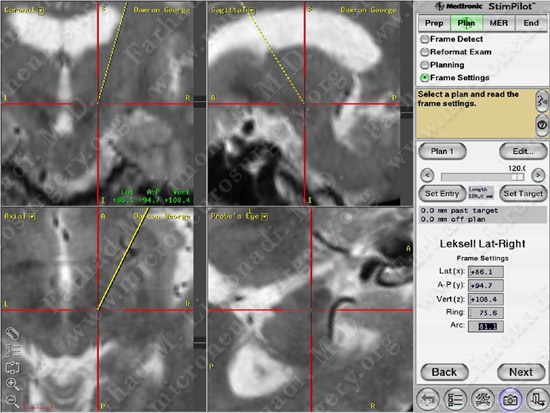
Stereotactic planning: anterior and posterior commissures are being marked.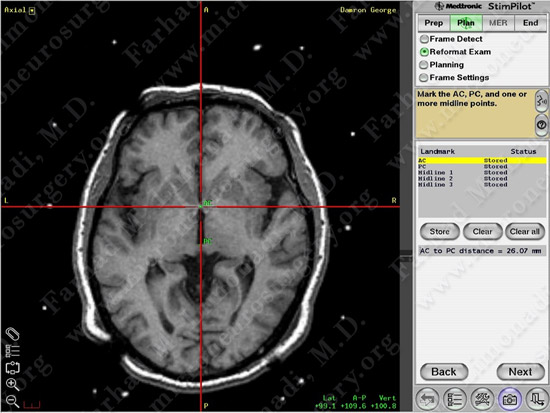
Anterior and posterior commissures are marked on the MRI.
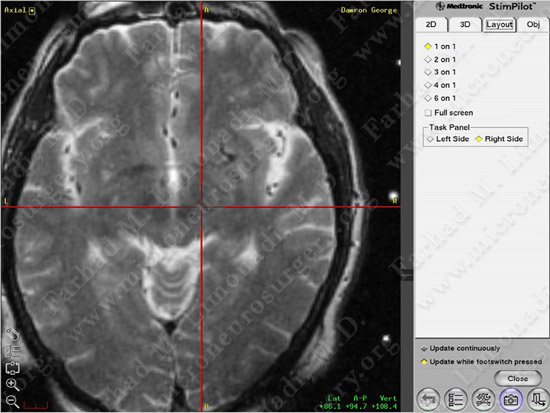
Subthalamic nucleus is identified and marked visually.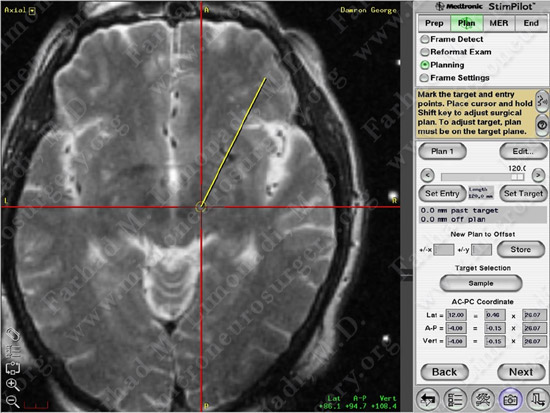
Surgical Procedure
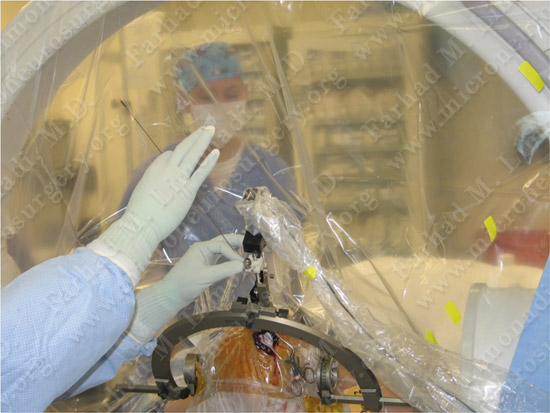
Microelectrode is being inserted along a trajectory to subthalamic nucleus for micro-recording while talking to the patient who is fully awake.
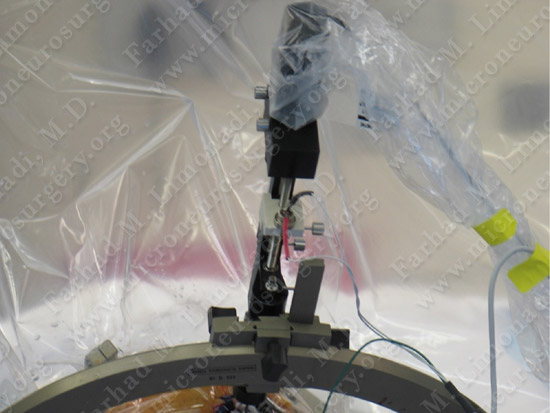

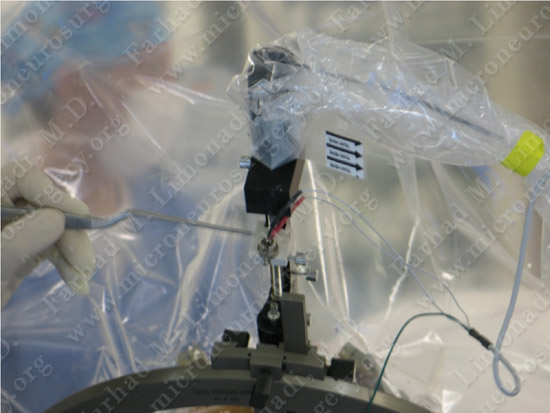
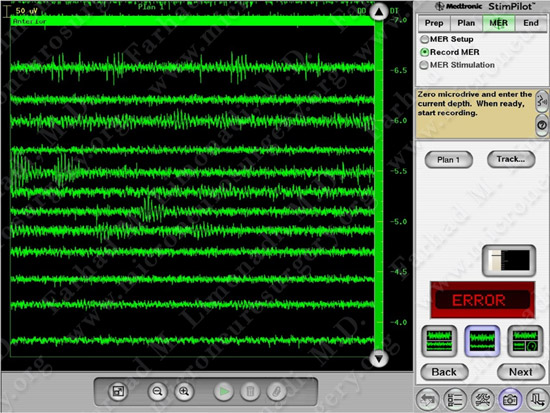
Microelectrode recording is utilized to confirm the location of subthalamic nucleus.
Post-op Imaging
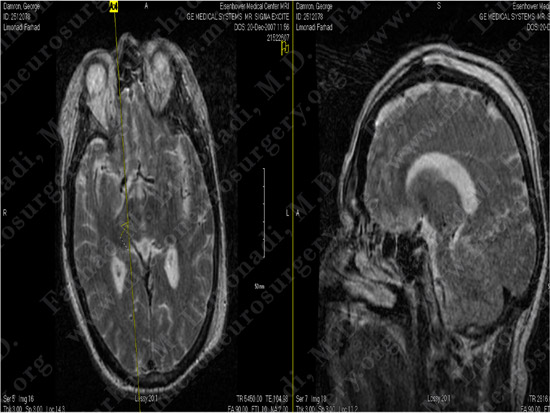
Post-op MRI confirms the precise position of the electrode within the subthalamic nucleus.
Post-op Course
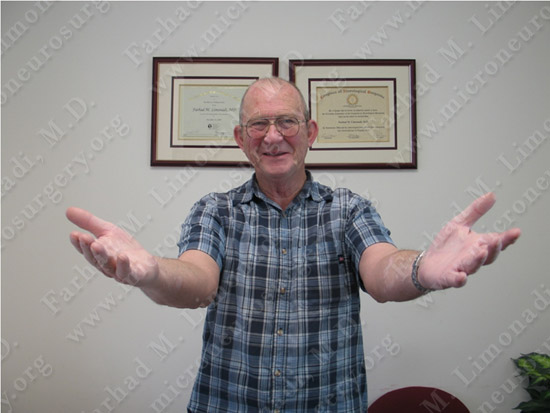


Patient’s tremor in left upper extremity nearly completely resolved after the operation.


















