Case Presentation:
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) - Awake Craniotomy - Case 10
History and Physical
- 63-year-old right handed lady with a known metastatic brain tumor (originated in the lung) located in the left motor strip resulting in focal seizure and right sided weakness.
- She had undergone radiosurgery to this tumor initially which resulted in tumor volume control for nearly 2 years. However, the tumor started to grow and cause hemiparesis (weakness on her right side) and focal seizure.
- On examination she had weakness of right side.
Imaging

MRI scan of patient's brain shows a tumor within the motor cortex gyrus.
Surgical Procedure
- She was indicated and underwent awake surgical resection of this tumor utilizing brain mapping, cortical stimulation, stereotactic and computer navigation, and intra-operative neurophysiological monitoring.
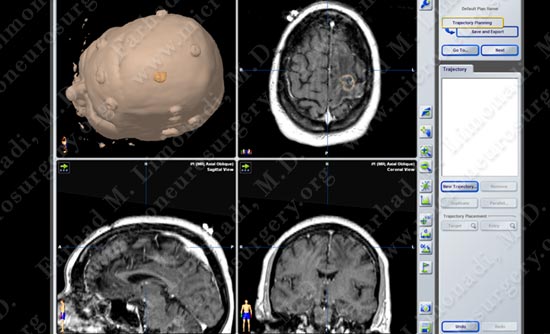
Computer navigation and stereotaxy utilized to map and localize the tumor (outlined in yellow) during surgery.
Computer navigation and stereotaxy utilized to map and localize the tumor (outlined in yellow) during surgery.
While patient is awake and conversing with Dr. Limonadi, motor cortex stimulation was utilized to locate the motor cortex.
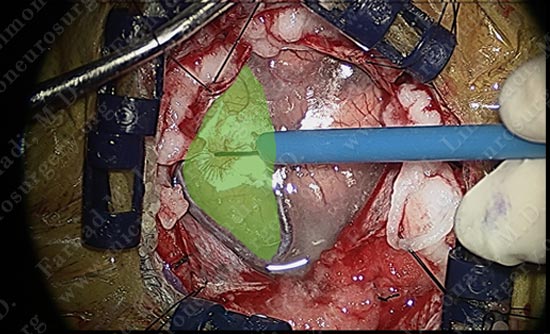
Motor cortex was identified and is colored green. The tumor is deep and within the parenchyma of this gyrus.
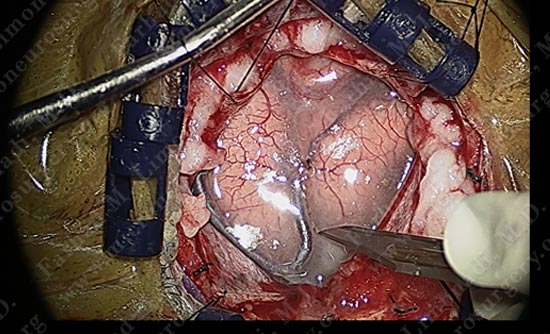
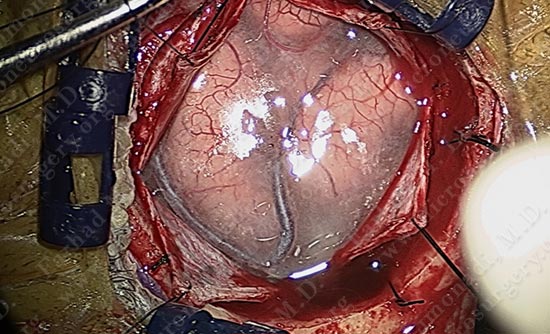
Using a scalpel, the arachnoid between the motor strip and adjacent gyrus is carefully opened without damaging the adjacent vessel.
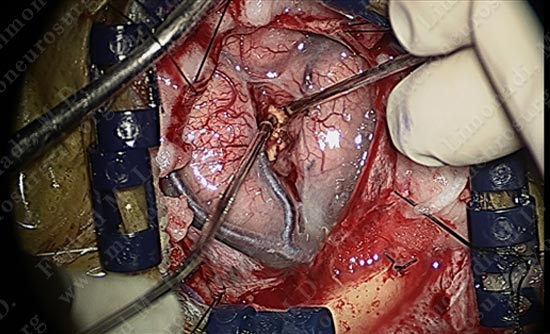
Micro-instruments are utilized in opening the interval between the two gyri underneath which the tumor is hidden. Patient is being examined in short intervals.
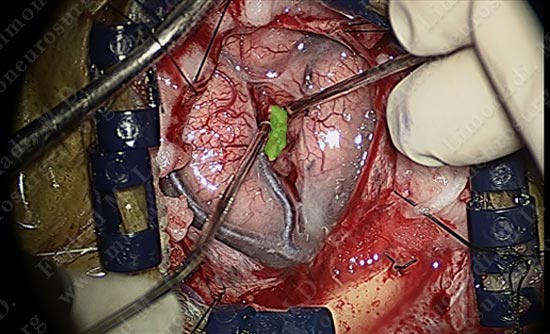
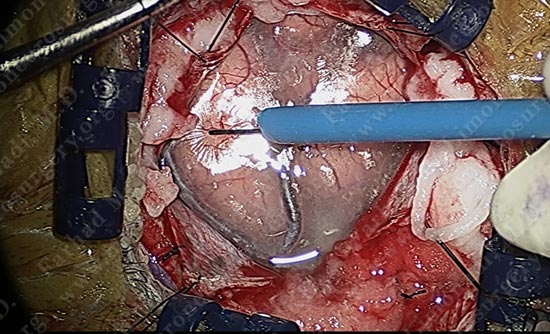
The superficial pole of the tumor is outlined in green.

Micro-instruments are utilized in opening the interval between the two gyri underneath which the tumor is hidden. Patient is being examined in short intervals.
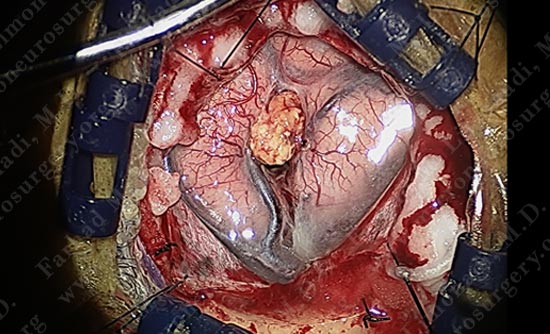
The tumor is nicely dissected out as patient is talking to the surgeon and being examined by the surgical team.
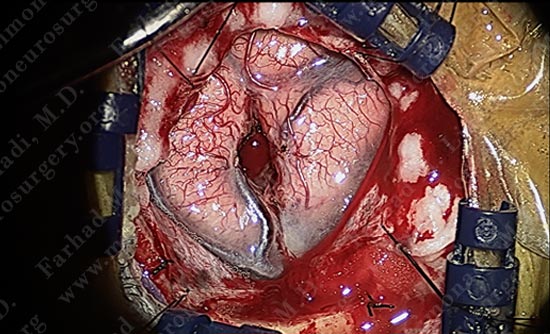
Tumor is removed without any injury to the motor cortex or adjacent neuro-vascular structures. Patient is awake and doing well with no neurological deficit.
Utilizing computer navigation, a small craniotomy was performed precisely over the tumor and the tumor was removed using this small opening.
Pathology
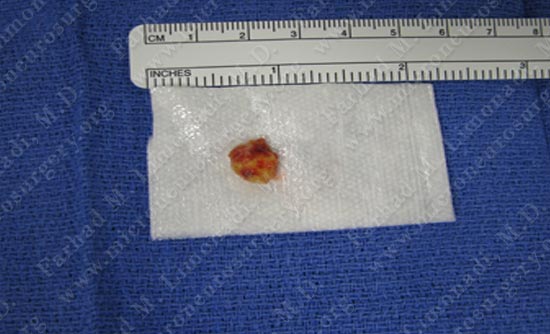
Tumor Specimen which was sent for pathological review
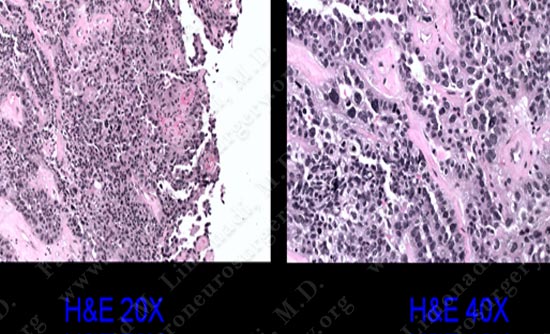
The pathology of the tumor confirmed diagnosis of metastatic adenocarcinoma.
Post-op Imaging
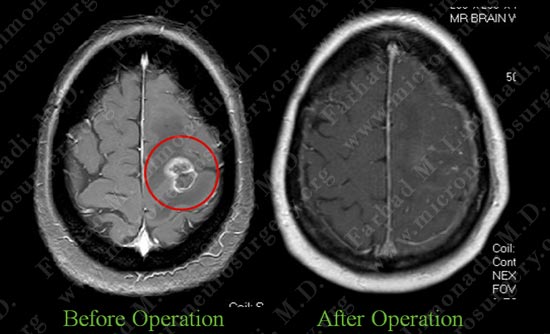
Post op MRI shows complete resection of the tumor with no injury to surrounding neuro-vascular structures. Most importantly patient had no neurological deficit after the operation.


















