Case Presentation:
Brain Stem Tumors - Case 1
Brain Stem Glioma and Hydrocephalus
History & Physical:
- A 36-year-old woman with one year history of headache and hypertension presented with diplopia, progressive headache, nausea and vomiting and loss of consciousness.
- MRI scan of her brain showed a tectal tumor obstructing the cerebral aqueduct and hydrocephalus. Patient underwent stereotactic endoscopic third ventriculostomy followed by gross total resection of the tectal tumor which was found to be anaplastic astrocytoma. She was discharged from the hospital neurologically intact and shunt independent
Computer Navigation
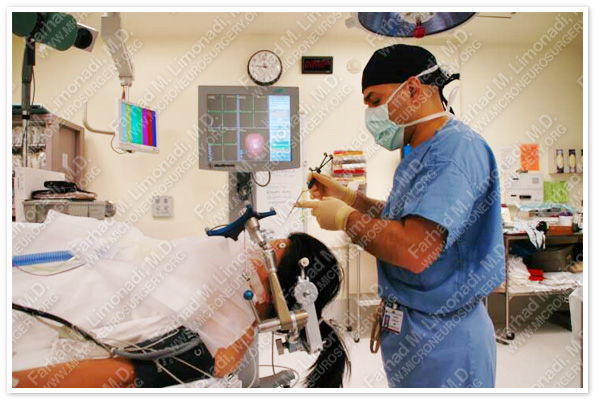
Patient is placed in a supine position on the operating table, and general anesthesia is induced. Her head is then fixed ina Mayfield head holder with 30 degrees elevation, and the coordinates of patient's brain are co-registered with the stereotactic navigation system.
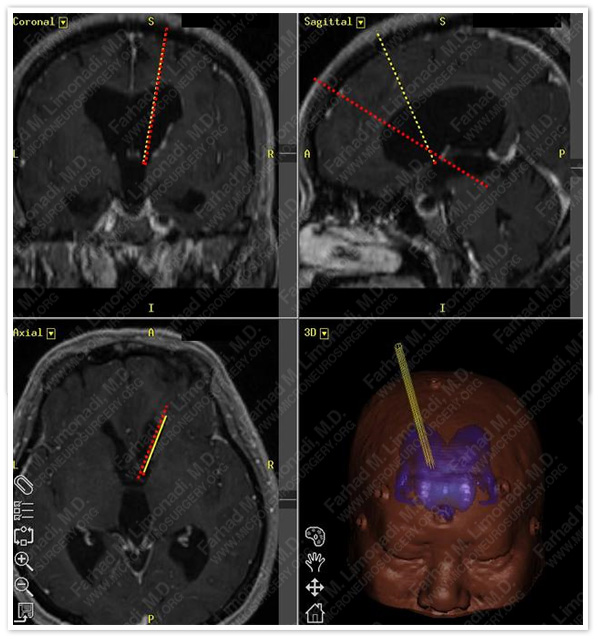
Two straight trajectories are meticulously planned using the preoperative MRI. The first one starts at the precoronal plane and slightly lateral from the midline (about 2 cm), goes through the foramen of Monro and ends at the floor of the third ventricle for the purpose of third ventriculostomy. If the starting point of this trajectory is too lateral, it could result in a lateral approach to the floor of the third ventricle and injury to theunderlying oculomotor nerve. The second trajectory, which bisects the first at the foramen of Monro, starts more anteriorly and ends at the tectal plate.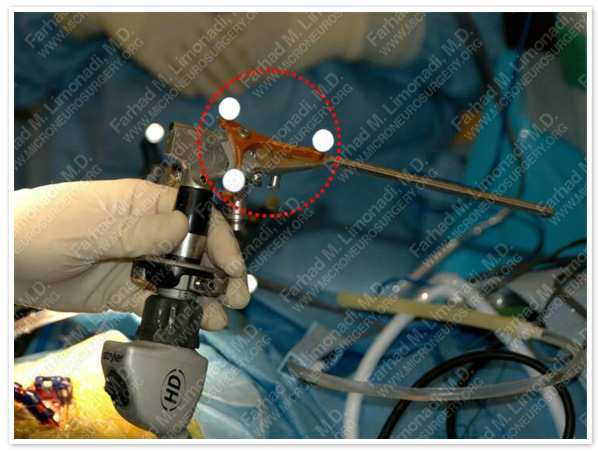
Patient's scalp is prepped and draped. A set of attachable Stealth stereotactic markers (Surtrak, Medtronics Inc., Minneapolis, MN) are attached to a neuroendoscope with 2.7 mm diameter inserted through a trocar, with a working distance of 15 cm and an outer diameter of 6 mm (Aesculap, Tuttlingen, Germany). The trocar is equipped with four channels: 1- endoscope, 2- instruments (e.g., forceps, micro scissors and bi-polar/mono-polar electrodes), 3- irrigation, and 4- outflow. The tip of the neuroendoscope is then registered to the Stealth navigation system. Therefore, the precise location of the tip of the neuroendoscope is well-defined and monitored in three dimensions of space.
Surgical Procedure
- Patient underwent stereotactic endoscopic third ventriculostomy followed by gross total resection of the tectal tumor which was found to be anaplastic astrocytoma.
Post-op Course
- She was discharged from the hospital neurologically intact and shunt independent.


















