Case Presentation:
Metastatic Lung Cancer - Case 4
- 76-year-old lady who with known diagnosis of primary pulmonary tumor (lung cancer). She presented with transient inability to speak (expressive aphasia), which prompted a 911 call and transport of the patient to the emergency room.
- On examination, she had generalized fatigue and no focal neurological deficit.
Imaging
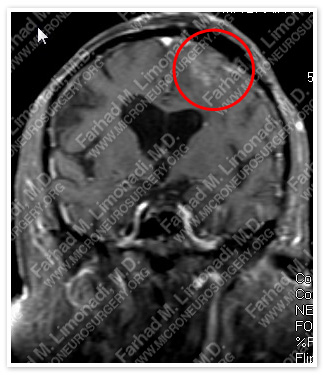
MRI scan of the patient’s brain showed a left frontal brain tumor.
Computer Navigation
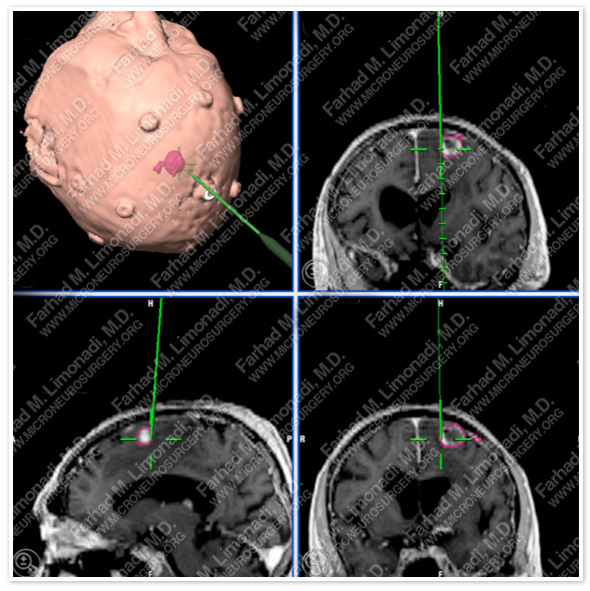
Computer navigation and stereotaxy utilized to map and localize the tumor (outlined in pink) during surgery.
Surgical Procedure
- She underwent surgical resection of this tumor using brain mapping, stereotactic and computer navigation, and intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring.
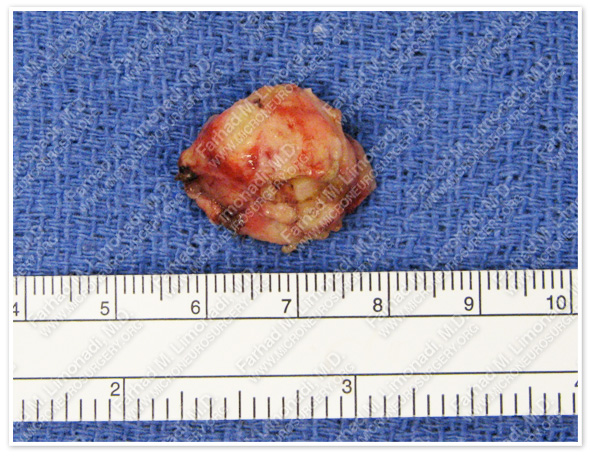
The tumor was removed in a gross total fashion.
PathoIogy
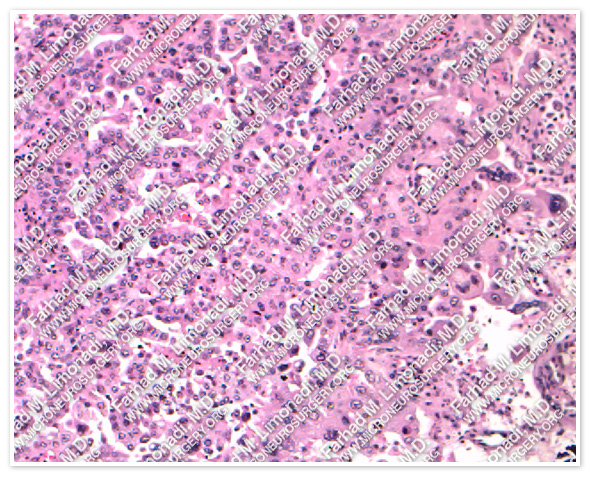
H & E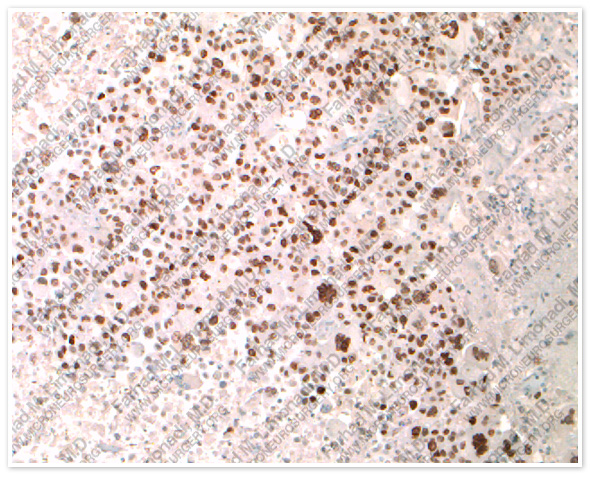
TTF-1
The pathology of the tumor confirmed diagnosis of metastatic lung cancer.
Post-op Imaging
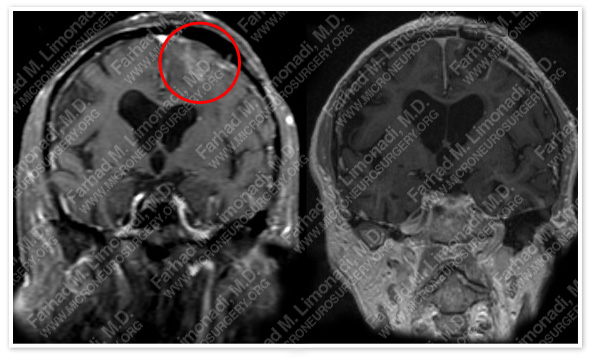 Before Operation After Operation
Before Operation After Operation
Post-op MRI shows complete resection of the tumor with no injury to surrounding neurovascular structures.
Post-op Course
- The patient did well postoperatively with return to base line neurological status. She was discharged from the hospital and proceeded with commenced definitive treatment of her lung cancer. She subsequently underwent stereotactic radiosurgery to the cavity at the tumor resection site to prevent any recurrence in this area.


















